Therapeutic plasma exchange (TPE), also known as plasmapheresis, is a medical procedure used to treat a range of autoimmune, hematological, neurological, and kidney disorders. It involves removing the plasma from a patient’s blood and replacing it with a substitute, either donor plasma or a plasma-like solution. The goal is to eliminate harmful substances in the blood that contribute to disease processes, such as autoantibodies, toxins, and other pathogenic proteins.
How Does Therapeutic Plasma Exchange Work?
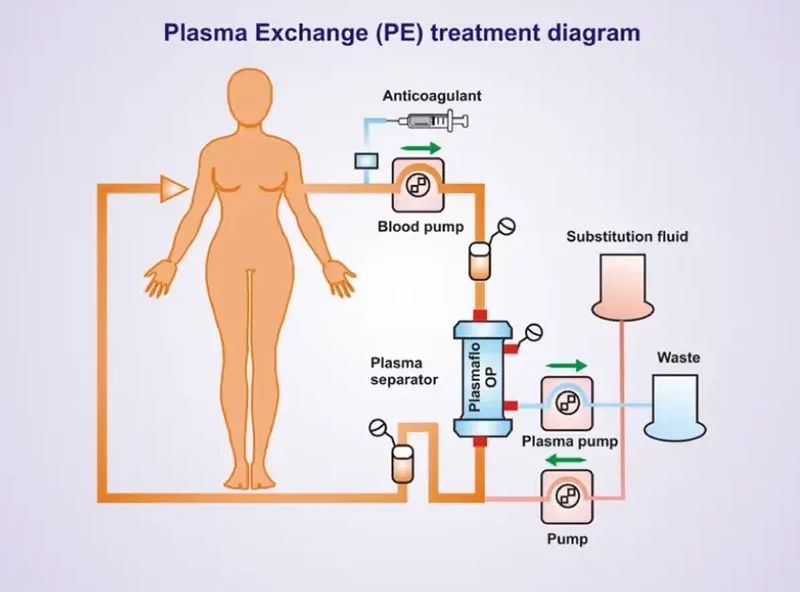
During the TPE process, blood is drawn from the patient through a needle or catheter and then separated into its individual components: red cells, white cells, platelets, and plasma. The plasma, which contains proteins, clotting factors, and antibodies, is removed because it may contain harmful substances that contribute to disease. The removed plasma is replaced with a substitute. Either donor plasma or a saline-albumin solution. Once the exchange is complete, the treated blood is returned to the patient’s body.
TPE sessions typically last two to four hours, depending on the patient’s condition and the volume of plasma being exchanged. Multiple sessions may be required depending on the specific condition being treated, and it is often used in conjunction with other therapies, such as immunosuppressive medications.
Conditions Treated with Therapeutic Plasma Exchange
TPE is used to manage a variety of disorders, particularly those in which the immune system is attacking the body’s own tissues or where harmful substances accumulate in the blood. Common conditions treated with TPE include:
- Neurological disorders: Guillain-Barré syndrome, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP), and multiple sclerosis.
- Hematological disorders: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP), a rare condition where blood clots form in small blood vessels throughout the body.
- Renal conditions: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis (FSGS), especially when there is a recurrence after kidney transplantation.
Autoimmune diseases: Myasthenia gravis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and vasculitis.
TPE vs. Other Apheresis Techniques
Therapeutic apheresis refers to a range of procedures that remove various components from the blood. TPE specifically targets the plasma, whereas other forms of apheresis remove different blood elements.
- Lipid apheresis focuses on removing low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, which can be beneficial for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia.
- Red blood cell exchange removes and replaces red blood cells to treat conditions such as sickle cell disease. At Mobil Dialysis, we only provide this service to our pediatric patients.
- Photopheresis collects and treats white blood cells for conditions like graft-versus-host disease.
Each of these therapies targets different aspects of the blood, depending on the disease in question.

Risks and Side Effects
While TPE is generally considered safe, there are some potential risks and side effects. These can include:
- Allergic reactions: Rare, but possible, especially when donor plasma is used as a replacement fluid.
- Low blood pressure: The process of removing and replacing plasma can sometimes result in drops in blood pressure.
- Infection: The use of intravenous catheters increases the risk of infection.
- Electrolyte imbalances: The exchange process can lead to fluctuations in electrolytes, which may need to be corrected during or after the procedure.
TPE is a highly individualized therapy. The frequency and duration of treatment depend on the underlying condition being treated and how the patient responds to the procedure. For instance, patients with acute conditions like Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura may require daily treatments over a short period, while those with chronic conditions like chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy may need regular treatments over an extended timeframe. In some cases, TPE is combined with other treatments such as immunosuppressive drugs to achieve optimal results.
Therapeutic plasma exchange is a valuable tool for managing several severe and often life-threatening conditions. By removing harmful substances from the plasma, it helps to mitigate disease progression and improve patients’ quality of life. As a non-invasive, well-tolerated treatment, TPE has become a cornerstone in managing conditions where the immune system plays a harmful role.





